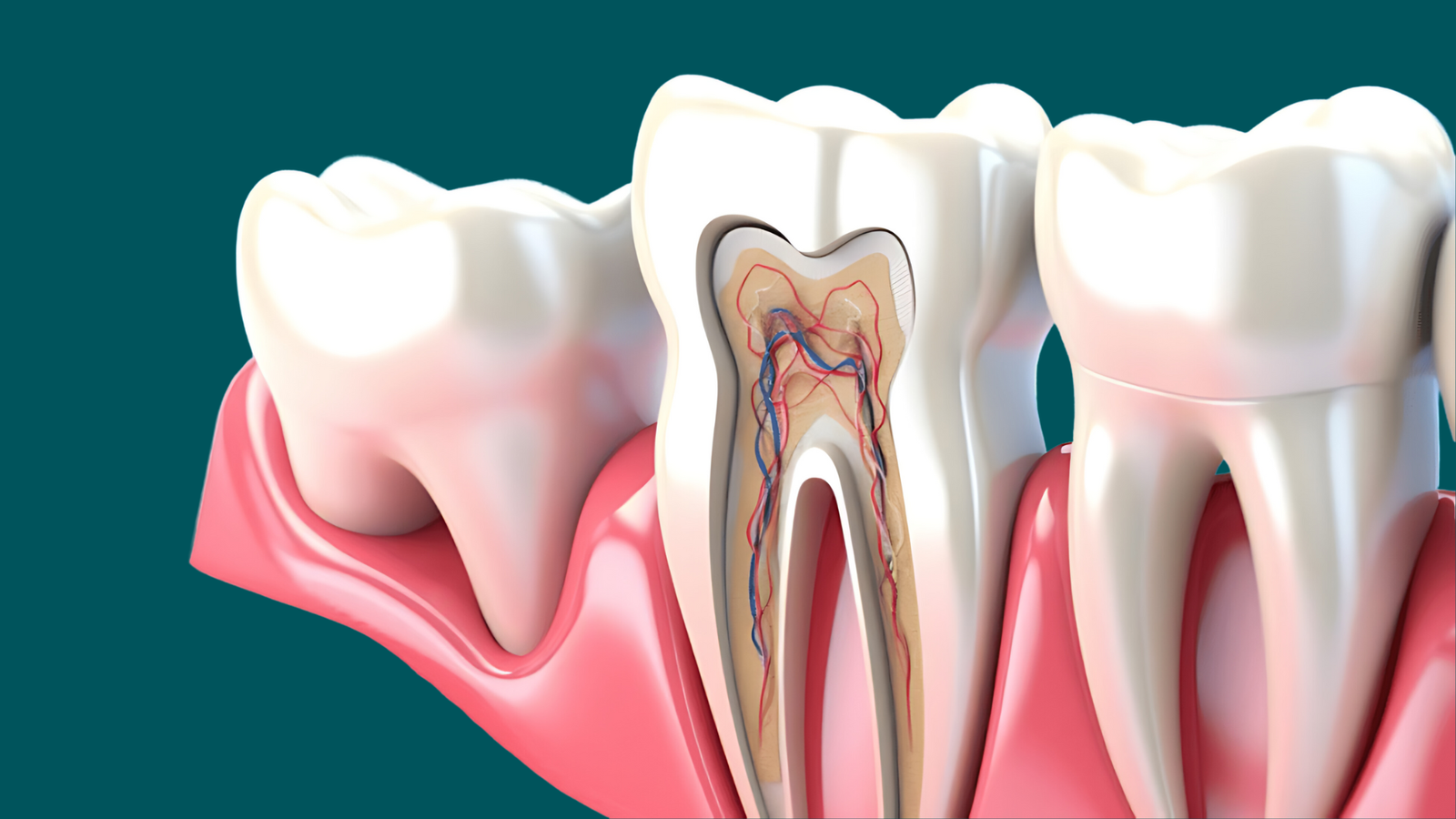
Pulpotomy
Maintaining the supply.
Discover more below.
Pain Relief
Tooth Preservation
Vitality Preservation
In a glance.
Consider When
- The tooth has extensive decay but the root is not affected.
- There is inflammation or infection in the pulp of a baby tooth or an immature adult tooth.
- The goal is to preserve the tooth for as long as possible.
Consider Other Options If
- The infection has spread to the roots, making a full root canal necessary.
- The tooth structure is severely compromised.
The Benefits
- Prevents the premature loss of baby teeth, which are important for proper chewing and space maintenance for permanent teeth.
- Offers a less invasive option compared to a full root canal.
- Can provide immediate relief from toothache.
The Drawbacks
- Not suitable for teeth with extensive root damage.
- May require further treatment if the initial infection is not fully contained.
Learn the process.
1. Initial Assessment
Assessment of the infected tooth through X-rays and tests to confirm the need for a root canal.
2. Decay Removal
Removing decay before accessing the root canal system is important to prevent spread of disease.
3. Pulp Removal
Infected pulp is carefully removed from the tooth.
4. Root Canal Shaping
The root canals are prepared and shaped to remove any infected portions and to provide sufficient space for the sealing material.
5. Disinfection and Dressing
The root canals are then disinfected and dressed with antibacterial materials for the overall success of the treatment.
6. Sealing
The now sterile canals are finally sealed and locked to prevent any recurrence of infection.
End of Root Canal Treatment
The root canal treatment concludes when the canals are sealed and the tooth no longer exhibits symptoms. Subsequent steps fall under "Restorative Dentistry," which focuses on restoring the tooth's final shape, structure, and functionality.
Post Placement
When there's limited tooth structure remaining due to significant damage, a dental post may be necessary. This post helps reinforce the tooth, providing the support needed for the final restoration.
Final Restoration
The selection of the final restoration is influenced by the remaining tooth structure, overall dental health, and personal preferences. Common options include dental crowns, direct fillings, and indirect fillings.
Learn More
The Scenario.
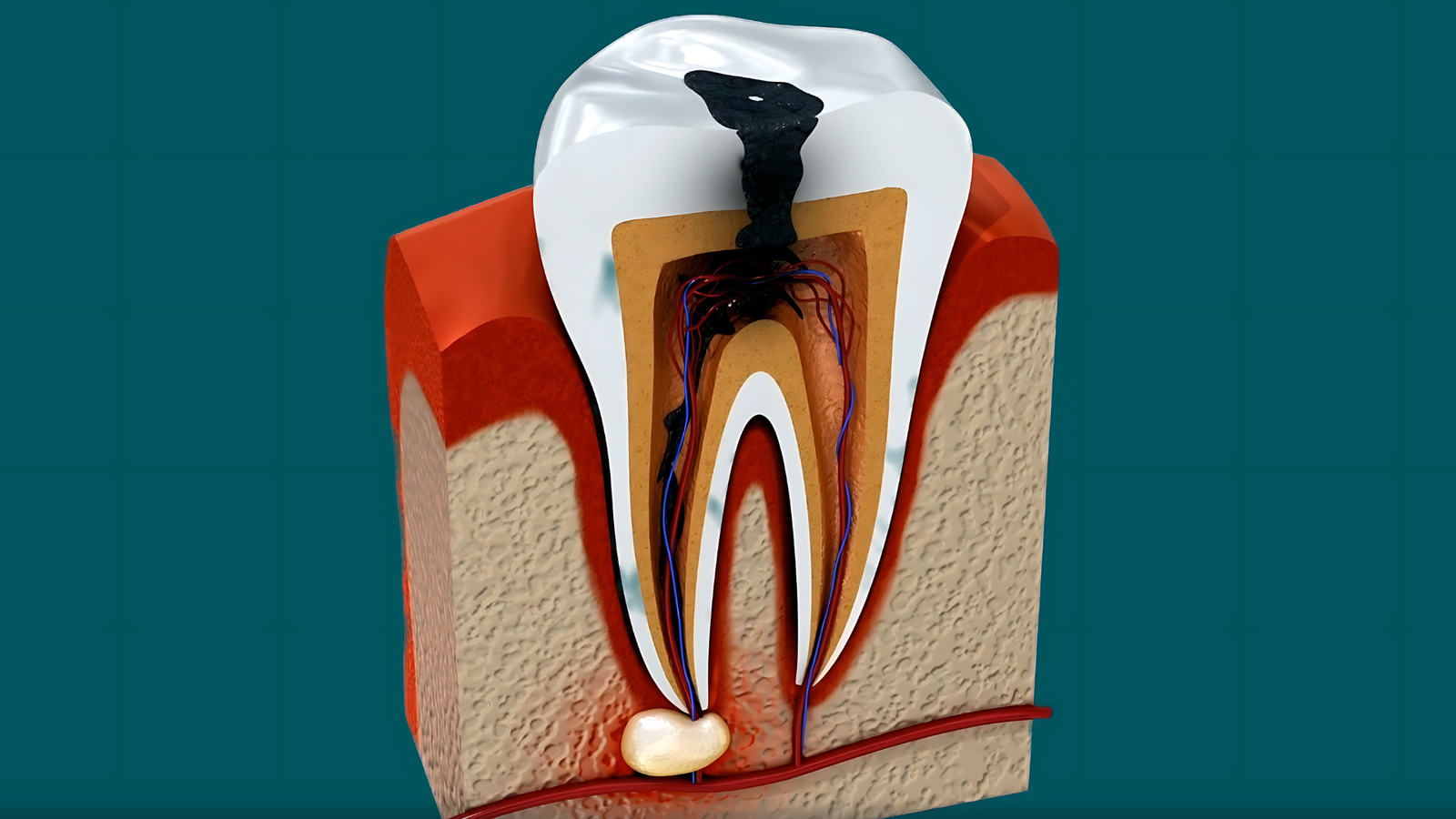
Regular dental checkups enable early detection, which can prevent complications that may otherwise necessitate endodontic treatment, or unfortunate tooth extraction.
The Solution.
What happens after a root canal treatment?
Crown
For teeth with extensive damage.
Indirect Filling
For teeth with moderate damage.
Direct Filling
For teeth with minimal damage.
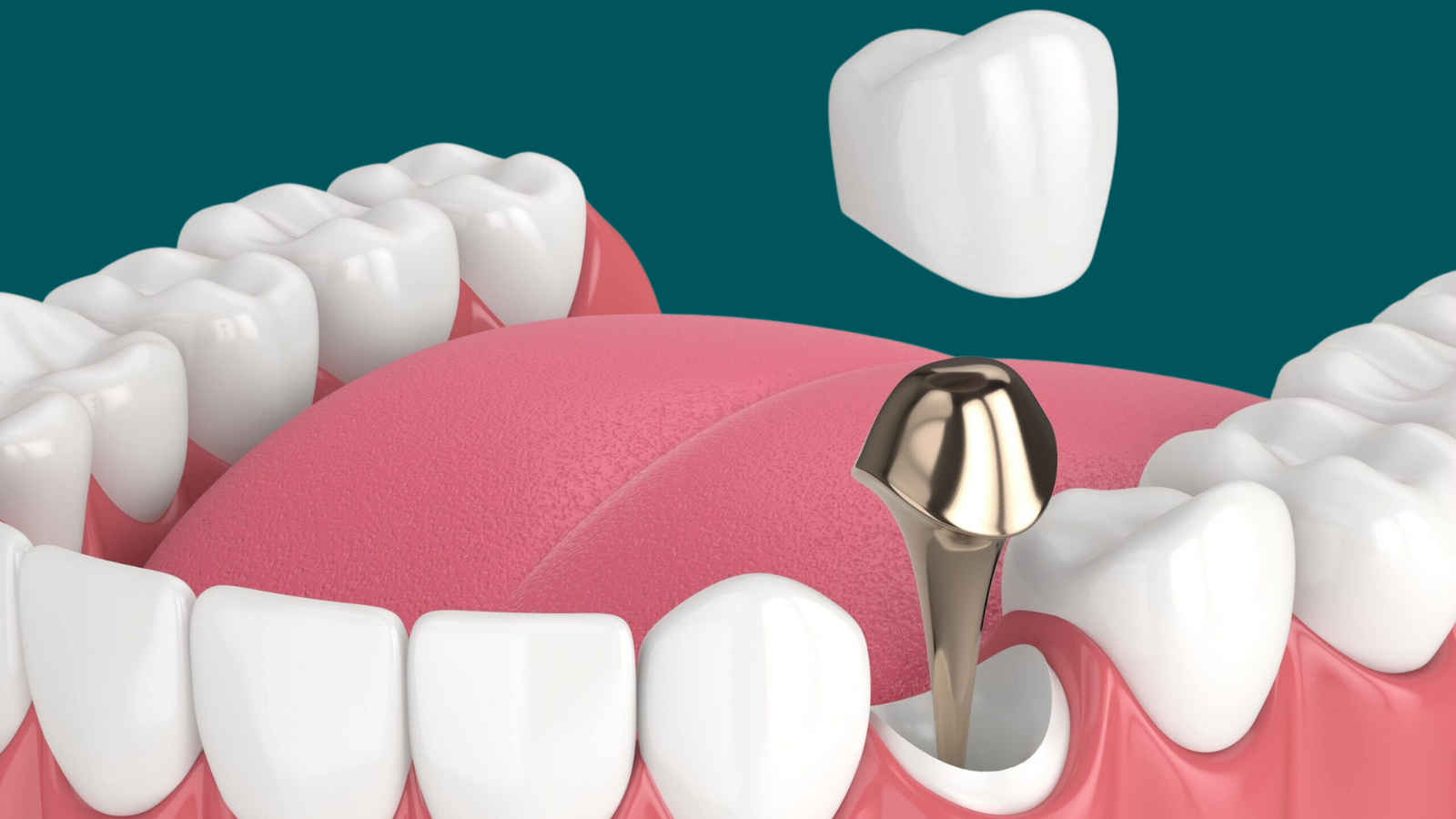
Dental Posts
Insufficient Tooth Structure?
In cases of substantial damage where tooth structure is compromised, a dental post becomes mandatory. This post plays a vital role in enforcing the tooth, ensuring adequate support and sufficient structure for the eventual restoration.
A message from Mirage Dental Clinic.
Steps and care.
Preventing further damage.
Before a root canal treatment
Between sessions
After root canal treatment
Frequently asked.
Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene can significantly reduce the risk.
- Some mild discomfort and sensitivity are normal but should subside within a few days.
With modern anesthesia and techniques, the procedure is typically painless, with discomfort managed effectively.
Speak with our dentists.
Alternative Options.
Discover other endodontic treatments that may be effective for you.